How Automated Key Kiosks & Dispatch Platforms Work
Understanding kiosk-based duplication, dispatch networks, and what they mean for modern locksmith businesses.
1. Introduction: Why This Model Exists
The locksmith and physical security industry has historically been defined by fragmentation. The market is composed largely of owner-operated businesses and small mobile fleets, with few national players possessing significant market share. In this environment, the primary challenge for local operators is not technical execution, but discoverability.
As digital customer acquisition costs (CAC) have risen—specifically the cost of Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising and Local Services Ads (LSA)—a gap has emerged for centralized platforms to enter the market. These platforms utilize capital-intensive infrastructure to aggregate consumer demand at scale.

The modern "hybrid" locksmith model combines physical automation with digital dispatch. In this framework, the automated key duplication kiosk serves a dual purpose: it is a point-of-sale device for simple retail transactions, but more importantly, it functions as physical distribution infrastructure.
Note: This demographic shift is creating a unique entry point for new technicians. See our full 2026 Career Outlook for salary projections and training requirements.
By placing hardware in high-traffic retail environments, companies secure a physical footprint that serves as an anchor for digital lead generation, effectively bypassing the traditional ad-spend wars that local locksmiths face.
2. The Two Revenue Streams Behind Kiosks
To understand the economic incentives of kiosk operators, it is necessary to distinguish between their two primary revenue streams. While the hardware is the most visible component, it often serves as a "loss leader" or low-margin entry point for a more lucrative service ecosystem.
A. Automated Key Duplication (High Volume, Low Ticket)
The primary function of the kiosk is to duplicate standard brass keys (residential and mailbox) and simple RFID fobs using robotics and computer vision.
- Unit Economics: Transactions typically range from $3.00 to $10.00.
- Strategic Role: Generates high-frequency consumer interactions and builds brand awareness.
B. Service Referrals & Dispatch (Lower Volume, High Margin)
When a customer presents a complex need—such as a modern automotive key requiring OBD programming, a residential lockout, or a lock installation—the kiosk interface directs them to a "partner" locksmith.
- Unit Economics: Services typically command prices ranging from $100 to $400+.
- Strategic Role: Captures high-intent leads at zero incremental marketing cost. The platform monetizes this by retaining a portion of the service fee.
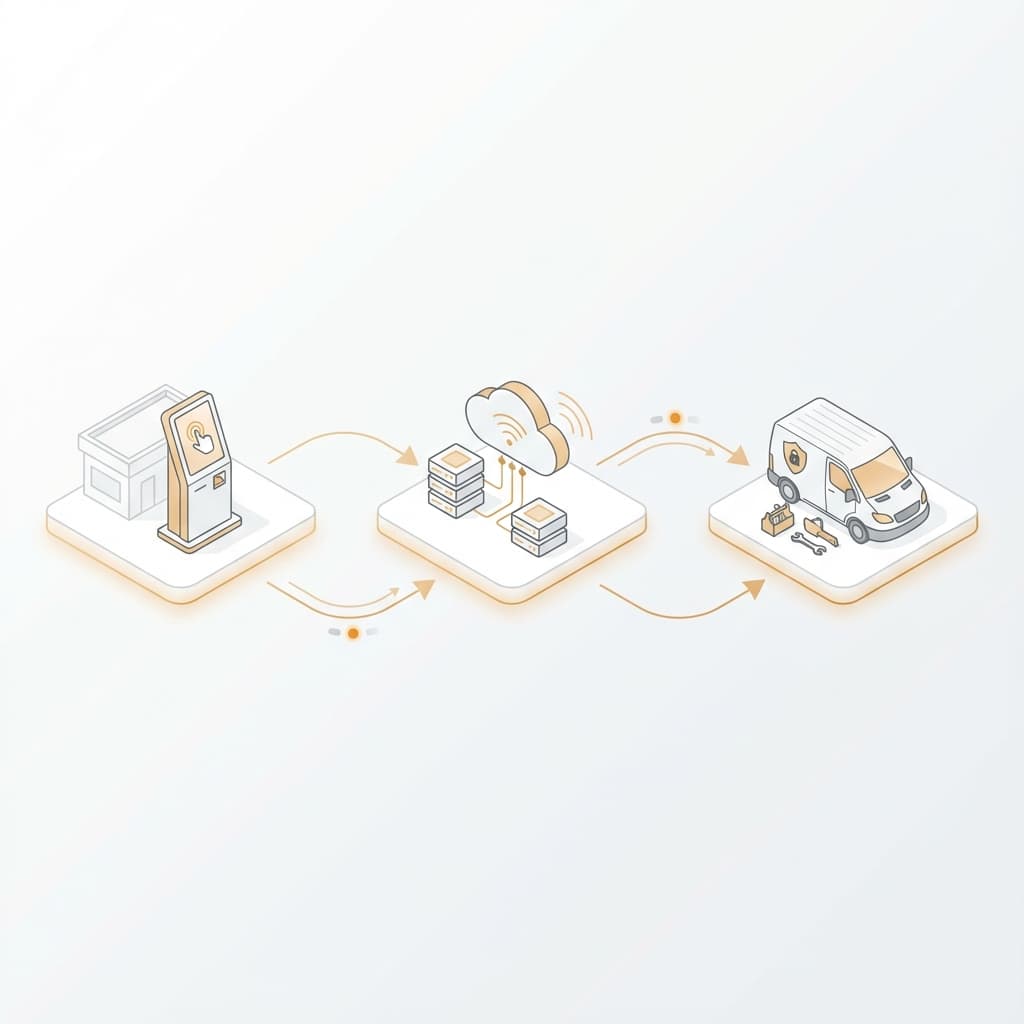
3. Dispatch-Based Aggregator Models
The "Dispatch-Aggregator" model fundamentally shifts the locksmith's role from a business owner who manages marketing and pricing to a subcontractor who focuses solely on fulfillment. Companies like KeyMe and MinuteKey have operationalized this structure to provide national coverage without owning service vehicles.
Operational Mechanics:
- Lead Capture: A customer contacts the platform via the kiosk, mobile app, or search engine result.
- Centralized Handling: A call center or algorithmic system quotes a standardized price.
- Fulfillment: The job is broadcast to verified local locksmiths who accept it at a "wholesale" rate.
For the Platform
Rapid scaling with minimal capital expenditure on fleets or employees.
For the Consumer
Standardized interface, 24/7 availability, and recognized brand convenience.
For the Technician
Steady work stream without advertising management, but at the cost of margin compression.
4. The Role of Physical Locations in Local Search
The viability of the dispatch model is heavily reliant on Local Search Engine Optimization (SEO). Major search engines prioritize "proximity" when ranking results for queries like "locksmith near me."
The Proximity Signal
To rank in the "Local Pack," a business needs a verified physical address. Purely mobile businesses often struggle to compete against competitors with physical storefronts.
- Kiosks as Micro-Warehouses: By placing kiosks in retail hubs, operators claim thousands of physical locations, signalling brand "proximity" even without on-site staff.
- Search Dominance: This strategy allows a national aggregator to appear as a hyper-local option in thousands of zip codes simultaneously.
5. How This Impacts Independent Locksmiths
The rise of aggregator models presents a strategic fork in the road for independent operators. For those struggling with marketing, aggregators offer immediate lead volume in exchange for a "marketing fee" (the reduced margin).
Participation Case
Access to guaranteed work without the overhead of building websites or managing Google Ads.
The Trade-Offs
- Pricing Autonomy: Technicians must accept rates dictated by the platform.
- Customer Ownership: Repeat business flows back to the app, not the technician.
- Margin Erosion: Continued market capture may permanently lower standard service pricing.
6. Alternative Models Emerging in the Industry
In response to high-commission dispatch models, alternative structures are emerging that aim to align incentives differently.
Subscription & Territory Models
Moving away from per-job splits to a "Digital Landlord" or flat subscription basis.
- Locksmith pays a flat monthly fee to "rent" a specific territory or kiosk location.
- Technician retains 100% of the revenue, restoring pricing power and brand value.
Software-First Enablement
White-label tools like Unlokt that give independent locksmiths national-level tech capabilities without ceding their identity.
- Automated booking, customer tracking, and sub-contractor management.
- Allows local owners to compete on efficiency without high lead-gen commissions.
7. Conclusion
The centralized dispatch model solves a real problem for consumers by reducing friction. However, for the trade operator, the decision to partner with an aggregator versus building an independent brand comes down to a calculation of unit economics. As the market matures, we expect to see large-scale national aggregators serving the convenience-focused mass market, and specialized independent operators utilizing subscription-based tools to serve the relationship-focused local market.
Transparency Update
This guide is for educational purposes. Unlokt primarily provides software to help independent locksmiths manage their own operations and brand. While we are developing a quality-focused network to connect consumers with top-tier local service members, we do not operate as high-commission dispatch aggregators.
